

An international team of scientists*, involving entomologists, conservation biologists, agro-ecologists and geographers, has just revealed how on-farm insect biological control can slow the pace of tropical deforestation and avert biodiversity loss on a macro-scale. The case study concerns biological control of the invasive mealybug Phenacoccus manihoti with the introduced host-specific parasitic wasp Anagyrus lopezi in Southeast Asia. The results of this study have just been published in Communications Biology – Nature.

Mealybug attack, Photo credit: Georgina Smith / CIAT
Though often perceived as an environmentally-risky practice, biological control of invasive species can restore crop yields, ease land pressure and contribute to forest conservation. This paper illustrates the positive impacts of Biological control when done properly and using the mealybug Phenacoccus manihoti (Hemiptera) in cassava as an example, Cassava is a key food, feed and fiber crop grown on around 4 million ha in tropical Asia where use of a parasitoid wasp decreases crop losses and consequently slows deforestation. This newly-arrived mealybug caused drops in Thailand’s cassava yields during 2009-2010, triggering sharp increases in cassava prices and spurring region-wide expansion of cassava crop surfaces. This coincided with 185-608% surges in peak deforestation rates in neighboring countries. Following release of the host-specific neotropical parasitoid Anagyrus lopezi (Hymenoptera) in 2010, mealybug outbreaks were reduced, the cropped area contracted, and the pace of deforestation slowed by 31-95% in individual countries. Hence, when used sensibly and according to established guidelines, biological control of a crop pest can avert the need for synthetic pesticides, shield tropical biodiversity and deliver long-lasting environmental benefits on a macro-scale.
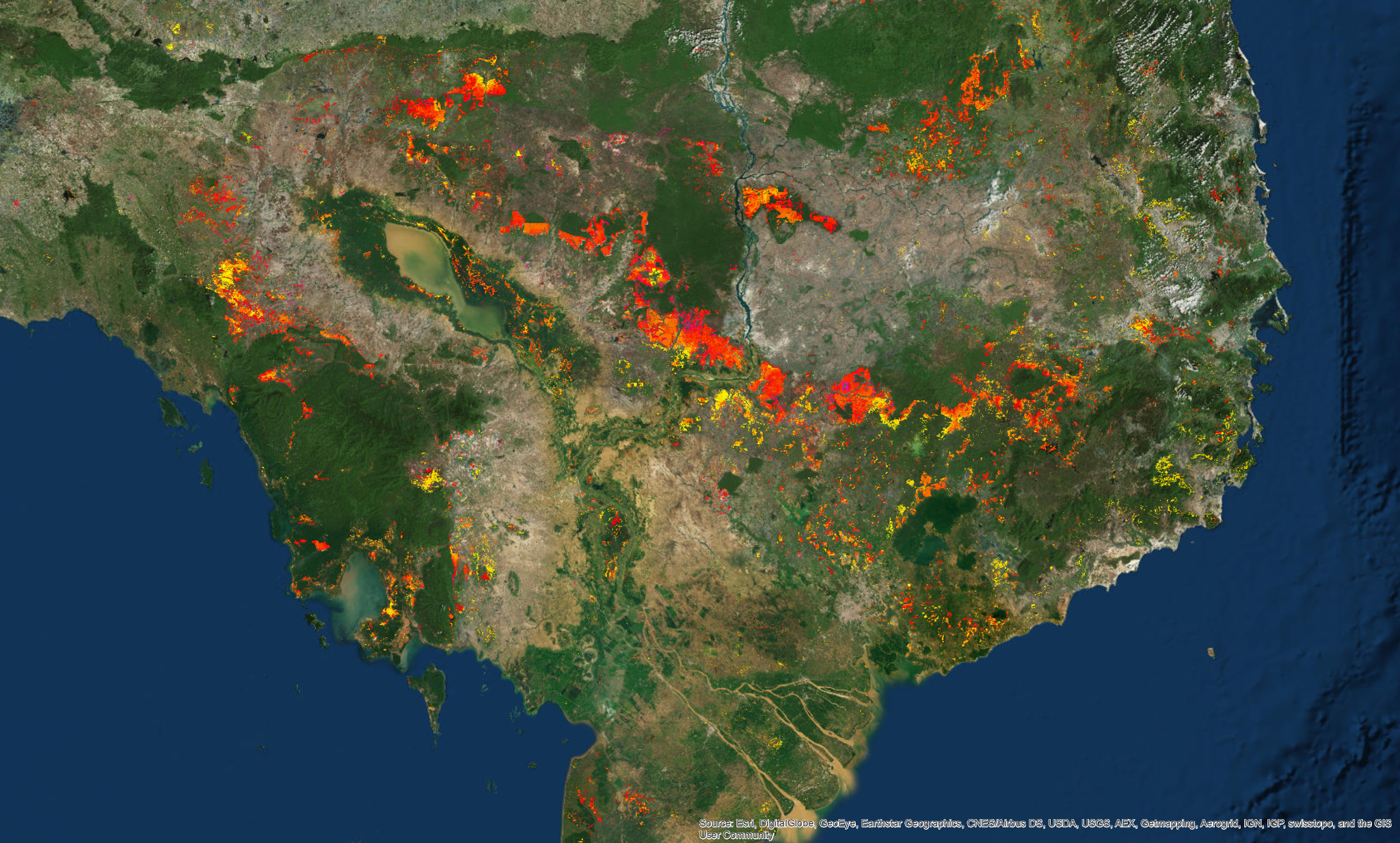
Expansion of the agricultural frontier & forest loss tracked with (near) real-time satellite imagery in Southeast Asia. Photo credit: Terra-i Project / CIAT
Insects provide invaluable services to humanity, including the natural control of agricultural pests, a service worth $4.5-17 billion annually to US agriculture alone. This study reveals how a judiciously-selected pest-killing insect – a minute parasitic wasp – helps resolve invasive pest problems, augments crop yields and protects tropical biodiversity. "Insect biological control reconnects insect friends and foes, and restores ecological balance in invaded agro-ecosystems", says Kris Wyckhuys, agro-ecologist at University of Queensland (Australia) and IPP-CAAS (China), and coordinator of the study. "Such nature-based approaches provide a self-sustaining ‘win-win’ solution that tackles invasive species mitigation, biodiversity conservation and profitable farming. Collaboration between conservation biologists and crop protection scientists can thus be beneficial to balance farmer realities on the ground with biodiversity conservation”.
This study underlines the ample environmental benefits of insect biological control, as a desirable alternative to insecticide-based approaches for tackling pest problems, supporting sustainable intensification and sparing land for conservation. "It is often difficult to reconcile socio-economic and ecological issues, and smallholder farmers are regularly tempted to resort to costly and environmentally damaging chemical pesticides to control pests. This study confirms that appropriate use of biological control can resolve socio-economic, environmental and ecological issues simultaneously, especially in tropical countries", adds Jean-Philippe Deguine, agro-ecologist and entomologist at CIRAD and co-author of the paper.
|
Agro-ecological Crop Protection, a way to preserve biodiversity in the tropics When used with established safeguards, biological control can permanently resolve invasive species problems. The scientifically-guided introduction of specialist natural enemies to provide pest control services in field crops is in line with agro-ecological crop protection. As a cost-effective alternative to pesticide-based approaches, and relying upon nature’s services to suppress crop pests, agro-ecological crop protection aims to restore and optimize ecosystem functioning and helps ensure that crop protection benefits farmers’ pockets, consumer and producer health and the broader farming environment. More information on agro-ecological crop protection in Southeast Asia: http://www.agriculture-biodiversite-oi.org/en/ACP-ACTAE/ |
Reference:
Wyckhuys K.A.G., Hughes A.C., Buamas C., Johnson A.C., Vasseur L., Reymondin L., Deguine J.-P., Sheil D., 2019. Biological control protects tropical forests. Communications Biology - Nature.
*Partners of the study:
- Institute of Applied Ecology, Fujian Agriculture & Forestry University, People’s Republic of China
- China Academy of Agricultural Sciences CAAS, Beijing, People’s Republic of China
- University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
- Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, People’s Republic of China;
- Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Gardens, China Academy of Sciences CAS, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, People’s Republic of China
- Department of Agriculture (DoA), Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, Bangkok, Thailand
- Charles Sturt University, Orange, NSW, Australia
- Brock University, St. Catharines (Ontario), Canada
- International Center for Tropical Agriculture CIAT – Asia regional office, Hanoi, Viet Nam
- CIRAD, UMR PVBMT, La Réunion, France
- Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Ås, Norway

The Terra-i team together with CRS El Salvador under the Raices project carried out a virtual workshop through the teams platform to technicians from the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources, CARITAS, Universidad El Salvador, CENTA, about the Mapping of land cover using remote sensors and open source tools such as GEE, SEPAL and QGIS- Plugin Semi Automatic Classification.

Near real-time vegetation loss detection in Southwestern Ethiopia: calibration, validation, and implementation of the Terra-i system

The Alliance of Bioversity International and the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT) (the Alliance) conducted a training for local stakeholders on the use of Terra-i as part of the collaboration with the Netherlands Development Organisation – SNV in the Coffee Agroforestry and Forest Enhancement for REDD+ (CAFÉ-REDD) Project.


IDENTIFICACIÓN DE CAUSAS DE PÉRDIDA DE COBERTURA VEGETAL EN LAS ÁREAS DE INTERVENCIÓN DE LA ACTIVIDAD GOBERNANZA EN ECOSISTEMAS, MEDIOS DE VIDA Y AGUA (USAID/GEMA) EN EL OCCIDENTE DE HONDURAS
MAPEO DE COBERTURAS DE LA TIERRA PARA EL 2017, EN EL OCCIDENTE HONDUREÑO SOBRE ÁREAS DE INTERVENCIÓN DE LA ACTIVIDAD GOBERNANZA EN ECOSISTEMAS, MEDIOS DE VIDA Y AGUA (USAID/GEMA)

CUANTIFICACIÓN DE LA DEFORESTACIÓN EN LAS ÁREAS DE INTERVENCIÓN DE LA ACTIVIDAD GOBERNANZA EN ECOSISTEMAS, MEDIOS DE VIDA Y AGUA (USAID/GEMA) EN EL OCCIDENTE DE HONDURAS

From May 8-12, 2017, the Terra-i team, together with staff from the DGOTA of Peru's Ministry of Environment, carried out the first field validation of vegetative land cover changes detected during Terra-i monitoring for 2016 and 2017, using the technology UAV. This work was carried out under the framework of the project “Sustainable Amazonian Landscapes”. The team carried out over-flights with a Phantom 3 advanced rotor drone and a fixed-wing Ebee drone in seven townships of Yurimaguas. The objective of this work was to recognize the dynamics of land cover and land use changes in the region while at the same time to validate the accuracy of the detections of forest loss being monitored by Terra-i in Yurimaguas.

CIAT and the Terra-i team are pleased to announce the publication of a new study in Paraquaria Natural, the most prestigious journal in Paraguay dedicated to biodiversity and the conservation of nature.

The Terra-i team has worked hard on renovating Terra-i’s website since early this year. A set of new features on the website provides interactive contents and facilitates adaptation to the mobile devices of our users. The fresh website was developed using the latest update of an open-source, Java-based web system, Magnolia CMS 5.4.4. This update was customized to add different categories of interaction such as news, vegetation cover changes, and information, among others.

Globally more than 1 billion people depend on forests for their livelihoods. Forests play a crucial role in climate regulation, ecosystem services provision and regulation, water supply, carbon storage and many other functions that support biodiversity. Currently the global rate of deforestation is substantial, and there is a growing need for timely, spatially explicit data that flag natural vegetation changes due to human activities.

New deforestation hotspots point the finger at my favourite fruit I love Terra-i, but today I hate it. A lot. The system uses satellite images to track deforestation in the Amazon in near-realtime. It’s extremely accurate: if a bunch of trees come down somewhere – no matter how remote – Terra-i picks it up. Cool, right? Not today. CIAT’s Louis Reymondin, the system’s chief architect, dropped the bombshell over coffee: it looks as though hundreds of hectares of rainforest in Peru are being trashed by… papaya.

The latest update of Terra-i has been used with the Co$ting Nature ecosystem services assessment tool to understand the impacts of recent forest loss in Colombia on biodiversity and ecosystem services.

The production of geospatial data related to land-use and land cover changes by governments and civil society organizations has vastly increased during the last decade. Going beyond the valuable information (location, rates and absolute values of changes) provided by these datasets, it is important to have a better understanding of the spatial configurations and composition of the detected change areas at multiple spatial resolutions and time periods. Alejandro Coca-Castro’s research is aiming to map types of spatial deforestation patterns in the Amazon rainforest through the integration of landscape fragmentation metrics and data mining techniques. The research will contribute to the understanding of two deforestation datasets (Terra-i and GFC) and is part of his master dissertation at King’s College London. This blog post highlights Alejandro’s research methodology, preliminary findings and challenges.

Ecuador is recognized as one of the biodiverse hotspots on earth, underneath the Amazon rainforest lies the country’s oil reservoir. With the oil companies and cleared routes come settlers, therefore more and more of this diverse rainforest is being cut down. Since the oil concerns entered the Ecuadorian Amazon 45 years ago, they keep exploring and exploiting the area. The Terra-i detections reveal a total habitat loss of 87,525 Ha, 16,943 Ha (19%) is part of protected areas, between January 2004 and February 2015.

IDENTIFICACIÓN DE CAUSAS DE PÉRDIDA DE COBERTURA VEGETAL EN LAS ÁREAS DE INTERVENCIÓN DE LA ACTIVIDAD GOBERNANZA EN ECOSISTEMAS, MEDIOS DE VIDA Y AGUA (USAID/GEMA) EN EL OCCIDENTE DE HONDURAS
MAPEO DE COBERTURAS DE LA TIERRA PARA EL 2017, EN EL OCCIDENTE HONDUREÑO SOBRE ÁREAS DE INTERVENCIÓN DE LA ACTIVIDAD GOBERNANZA EN ECOSISTEMAS, MEDIOS DE VIDA Y AGUA (USAID/GEMA)

CUANTIFICACIÓN DE LA DEFORESTACIÓN EN LAS ÁREAS DE INTERVENCIÓN DE LA ACTIVIDAD GOBERNANZA EN ECOSISTEMAS, MEDIOS DE VIDA Y AGUA (USAID/GEMA) EN EL OCCIDENTE DE HONDURAS

CIAT and the Terra-i team are pleased to announce the publication of a new study in Paraquaria Natural, the most prestigious journal in Paraguay dedicated to biodiversity and the conservation of nature.

New deforestation hotspots point the finger at my favourite fruit I love Terra-i, but today I hate it. A lot. The system uses satellite images to track deforestation in the Amazon in near-realtime. It’s extremely accurate: if a bunch of trees come down somewhere – no matter how remote – Terra-i picks it up. Cool, right? Not today. CIAT’s Louis Reymondin, the system’s chief architect, dropped the bombshell over coffee: it looks as though hundreds of hectares of rainforest in Peru are being trashed by… papaya.

The production of geospatial data related to land-use and land cover changes by governments and civil society organizations has vastly increased during the last decade. Going beyond the valuable information (location, rates and absolute values of changes) provided by these datasets, it is important to have a better understanding of the spatial configurations and composition of the detected change areas at multiple spatial resolutions and time periods. Alejandro Coca-Castro’s research is aiming to map types of spatial deforestation patterns in the Amazon rainforest through the integration of landscape fragmentation metrics and data mining techniques. The research will contribute to the understanding of two deforestation datasets (Terra-i and GFC) and is part of his master dissertation at King’s College London. This blog post highlights Alejandro’s research methodology, preliminary findings and challenges.

Ecuador is recognized as one of the biodiverse hotspots on earth, underneath the Amazon rainforest lies the country’s oil reservoir. With the oil companies and cleared routes come settlers, therefore more and more of this diverse rainforest is being cut down. Since the oil concerns entered the Ecuadorian Amazon 45 years ago, they keep exploring and exploiting the area. The Terra-i detections reveal a total habitat loss of 87,525 Ha, 16,943 Ha (19%) is part of protected areas, between January 2004 and February 2015.